Microsoft Word Auto-Journal Macro for the Lazy
Kyle Niewiada on March 14, 2016
3 Minute Read | Small project
Updated on October 01, 2021
A few months back I was given the requirement for a project to keep some kind of journal logging the number of hours I spent on a task along with a short description. Because the project was deeply integrated with Microsoft products and services, I decided that it would be best to write such a journal with Microsoft Word.
As is the motivation for many projects/scripts of mine, I wanted to automate the process as much as possible such that I never had to think about it again [anytime soon]. This was shortly after I had concluded work on a previous project that involved using Microsoft Word with macro scripts. I was ready to learn more about its advanced features. I wanted an automatic running total because I would often forget to recalculate my grand total after each entry. There were probably other solutions that were better suited for this, but I really wanted to see how useful Microsoft Word macros (I know the evil stigma associated with macros) could be to me.
Goals:
- Automatically insert a new blank entry for today with the cursor ready to write a description
- The ability to total hours for all entries without the user remembering
- Automatically update total hours at top of document
Results:
I created a Microsoft Word macro enabled document that when opened will:
- Automatically remove empty paragraphs that Microsoft Word loves to place at the end of your document
- Add skeleton text containing today’s date, start, end, and total time
- Add a paragraph labeled “Description:”
- Calculate total hours on exit without user needing to remember
- Automatically add skeleton entry on document open
What it does
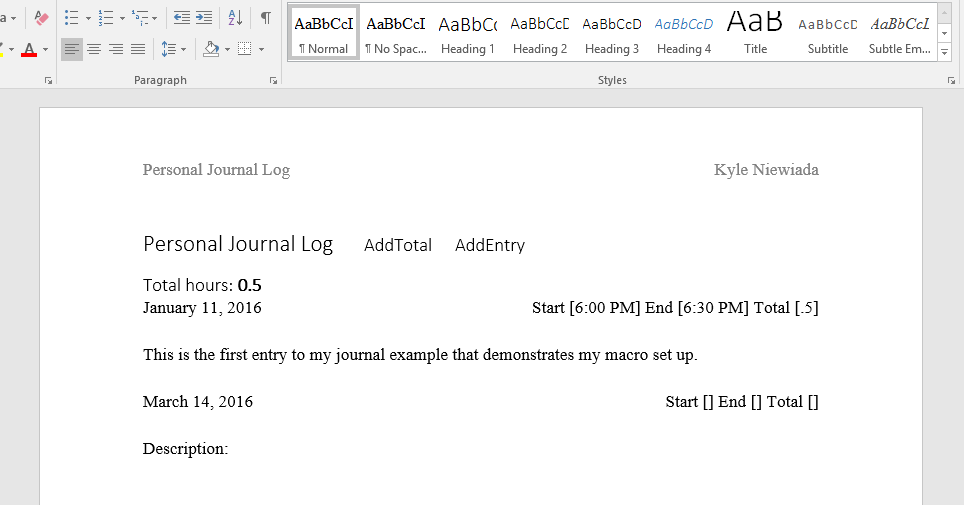
I have provided an example document below. It includes a text-button to add the total number of hours for each entry and another text-button to add new journal entries.
The macro calculates the total number of hours entered by searching for the ‘Total [*]’ string. When it matches, it will add the number found between ‘[]’ to a running total until the entire document has been searched. It will then return the total. The example document shows this total at the top. It is not foolproof. It can be easily defeated if someone decides to include the ‘Total [*]’ string inside their journal entry, or if one wants to overflow the numbers. But it works for me without any major issues (including the null value case), and that is what mattered.
The macro adds a new journal entry to the end of the text by searching for the end of the document, removing any extra paragraphs at the end of the document, and then adding in the pre-scripted skeleton structure for a new journal entry with the date of today. During planning, I could have gone above and beyond and calculated the total hours between the start time and end time of a task/added it to the ‘Total []’ field, but I decided to draw the line there. The amount of work I was putting in for something that would take no time to accomplish would not be paying off.
When the document is closed, the macro will run and add up the total number of hours from the listed entries automatically. A save dialog will then pop up and the user may choose to save or discard changes.
Source code and example document
Microsoft Word Auto-Journal example document
Above is a link to the macro enabled Microsoft Word document example. Below is the source code for the macro. Most of it is pieced together from other examples online accomplishing similar tasks. I spent most of my time looking at different resources for visual basic techniques and have mentioned those sources in nearby comments for pieces of code where available.
Sub AutoOpen()
Call autoText
End Sub
'Generate form fill text for document on call
Sub autoText()
'remove the empty paragraph that word likes to add to the end of the document on open.
Call removeEmptyPara
Selection.EndKey Unit:=wdStory
Selection.TypeParagraph
Selection.InsertDateTime DateTimeFormat:="MMMM dd, yyyy", _
InsertAsField:=False
Selection.TypeText vbTab & "Start [] End [] Total []"
Selection.EndKey Unit:=wdStory
Selection.TypeParagraph
Selection.TypeText "Description: "
End Sub
'Removes empty paragraphs located at the end of the document
Sub removeEmptyPara()
'https://www.extendoffice.com/documents/word/647-word-remove-empty-paragraphs.html
Selection.Find.ClearFormattin
Selection.Find.Replacement.ClearFormatting
With Selection.Find
.Text = "^p^p"
.Replacement.Text = ""
.Forward = True
.Wrap = wdFindContinue
.Format = False
.MatchCase = False
.MatchWholeWord = False
.MatchByte = False
.MatchAllWordForms = False
.MatchSoundsLike = False
.MatchWildcards = False
.MatchFuzzy = False
End With
Selection.Find.Execute Replace:=wdReplaceAll
End Sub
Sub AutoClose()
Call findTotal
End Sub
Sub findTotal()
'based on https://stackoverflow.com/questions/6425595/word-vba-how-to-select-text-between-two-substrings-and-assign-to-variable
Dim firstTerm As String
Dim secondTerm As String
Dim myRange As Range
Dim documentText As String
Dim startPos As Long 'Stores the starting position of firstTerm
Dim stopPos As Long 'Stores the starting position of secondTerm based on first term's location
Dim nextPosition As Long 'The next position to search for the firstTerm
Dim total As Double
total = 0
nextPosition = 1
firstTerm = "Total ["
secondTerm = "]"
'Get all the document text and store it in a variable.
Set myRange = ActiveDocument.Range
'Maximum limit of a string is 2 billion characters.
'So, hopefully your document is not bigger than that. However, expect declining performance based on how big doucment is
documentText = myRange.Text
'Loop documentText till you can't find any more matching "terms"
Do Until nextPosition = 0
startPos = InStr(nextPosition, documentText, firstTerm, vbTextCompare)
stopPos = InStr(startPos, documentText, secondTerm, vbTextCompare)
'prevents empty brackets from crashing macro
If stopPos - startPos <> Len(firstTerm) Then
'Debug.Print Mid$(documentText, startPos + Len(firstTerm), stopPos - startPos - Len(firstTerm))
total = total + Mid$(documentText, startPos + Len(firstTerm), stopPos - startPos - Len(firstTerm))
End If
nextPosition = InStr(stopPos, documentText, firstTerm, vbTextCompare)
Loop
Debug.Print "Total = "; total
ActiveDocument.Variables("total").Delete
ActiveDocument.Variables.Add Name:="total", Value:=total
'MsgBox "I'm done"
Call UpdateAll
End Sub
Sub UpdateAll()
'Based on unknown source.
Dim oStory As Range
For Each oStory In ActiveDocument.StoryRanges
oStory.Fields.Update
If oStory.StoryType <> wdMainTextStory Then
While Not (oStory.NextStoryRange Is Nothing)
Set oStory = oStory.NextStoryRange
oStory.Fields.Update
Wend
End If
Next oStory
Set oStory = Nothing
End Sub

